Cost accounting is defined as ” the process of accounting for cost which begins with recording of income and expenditure or the basis on which they are calculated & ends with the preparation of periodical statements and reports of ascertaining and controlling costs.”
Index
1. What is the meaning of cost and cost accounting?
2. What are the objectives of cost accounting?
3. What are the advantages of cost accounting?
4. What are the limitations of cost accounting?
5. Techniques of cost accounting.
1. What is the meaning of cost and cost accounting?
Cost:
Cost is the amount of resources given up in the exchange of some goods or services. It can be expressed as noun as well as verb. As a noun , it can be defined as the amount of expenditure incurred on or attributable to a specified article, product or activity.
Further, as a verb , it can be as an action to ascertain the cost of a specified thing or activity.
Costing is defined as ” the technique and process of ascertaining costs.”
Whereas ,
Cost accounting:
It is defined as ” the process of accounting for cost which begins with recording of income and expenditure or the basis on which they are calculated & ends with the preparation of periodical statements and reports of ascertaining and controlling costs.”
In other words, it is an application of management accounting concepts, methods of collections, analysis and presentation of data to provide information needed to plan , monitor and controls costs.
2. What are the objectives of cost accounting?
The main objectives of cost and management accounting are explained below:
1.Ascetainment of cost:
The main objectives of cost accounting is accumulation and ascertainment of cost. Moreover, costs are accumulated, assigned and ascertainment for each cost object. Further, this cost object may be a unit, job, operation, process, department or service.
2. Determination of selling price and profitability:
It is system helps in determination of selling price and thus profitability of a cost object. Though in a competitive business environment selling prices are determined by external factors but cost accounting system provides a basis for price fixation and rate negotiation.
3. Cost Control:
Maintaining discipline in expenditure is one of the main objectives of a good cost accounting system. Further, it ensures that expenditures are in consonance with predetermined set standard and any variation from these set standards is noted and reported on continues basis.
To exercise control over cost , following steps are followed:
- Determination of pre-determined standard or results
- Measurement of actual performance
- Comparison of actual performance with the set standard or target
- And, analysis of variance and action
4. Cost reduction:
It may be defined “as the achievement of real and permanent reduction in the unit cost of goods manufactured or services rendered without impairing their suitability for the use intended or diminution in the quality of the product”.
Cost reduction is an approach of management where cost of an object is believed to have a scope of further reduction. Further, no cost is termed as lowest and every possibility of cost reduction is explored.
However, to do cost reduction , following action is taken:
- Each activity within an entity is segmented to analyze and identify value added and non- value added activities. Moreover, all non-value added activities are eliminated without affecting the essential characteristics of the product or process. Further, value chain analysis a strategic tool developed by Michal porter is one of the method to do value analysis.
- Conducting continues research and study to know the most optimal way to manufacture a product or render a service.
However, 3 fold assumption involved in the definition of cost reduction may be summarized as under:
- There is saving in unit cost
- Such saving in permanent in nature
- And, the utility and quality of the goods and services remain unaffected , if not improved
5. Assisting management in decision making:
Cost and Management accounting by providing relevant information, assist management in planning, implementing, measuring, controlling and evaluating of various activities. Further, a robust cost and management accounting system provides internal and external information to the industry which will be relevant for decision making.
3. What are the advantages of cost accounting?
Following are the advantages of cost accounting:
- It provides relevant information to management for decision making.
- Further, it assist in allocation of costs to products and inventories.
- Cost accounting helps to know the profitability – product wise , department wise or customer wise etc.
- Assist in evaluating the strategic options to make decisions.
- Helps in deciding the cost of goods or services precisely.
- It assist in deciding the selling price of the goods or services.
- Lastly, helps in complying the legal and regulatory requirements.
4. What are the limitations of cost accounting?
The limitations are as follows:
- Expensive: It is expensive because analysis, allocation and absorption of overheads requires considerable amount of additional work, and hence additional money.
- Requirement of reconciliation : The results shown by cost accounts differ from those shown by financial accounts. Thus preparation of reconciliation statements is necessary to verify their accuracy.
- Duplication of work: It involves duplication of work as organization has to maintain two sets of accounts i.e. Financial Accounts nd Cost Accounts.
5. Techniques of cost accounting.
For ascertaining cost, following types of costing are usually used:
1. Uniform Costing:
When a number of firms in an industry agree among themselves to follow the same system of costing in detail, adopting common terminology for various items and processes they are said to follow a system of uniform costing.
2. Marginal costing:
Marginal costs as understood in economics is the incremental cost of production which arises due to one-unit increase in the production quantity .
Further, as we understood variable costs have direct relationship with volume of output and fixed cost remains constant irrespective of volume of production.
Hence, the marginal costs are measured by the total variable cost attributable to one unit. Thus, marginal cost is precisely sum of prime cost and variable overhead.
3. Standard costing:
It is the name given to the technique whereby standard costs are pre-determined and subsequently compared with the recorded actual costs. It is thus a technique of cost ascertainment and cost control .
4. Historical costing:
It is the ascertainment of costs after they have been incurred. It means ascertainment of cost after production is completed.
5. Absorption costing:
It is the practice of charging all costs, both variable and fixed to operations, process or products. This differ from marginal costing where fixed costs are excluded.
You can refer: https://taxandfinanceguide.com/marginal-costing/

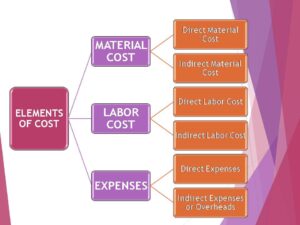

[…] Refer: https://taxandfinanceguide.com/cost-accounting/ […]